relay protection test
A relay protection tester is a device used to test the operation of protective relays in electrical systems. Protective relays are critical components that automatically disconnect faulty parts of the power system to prevent damage to equipment and ensure the safety of the electrical network.
-
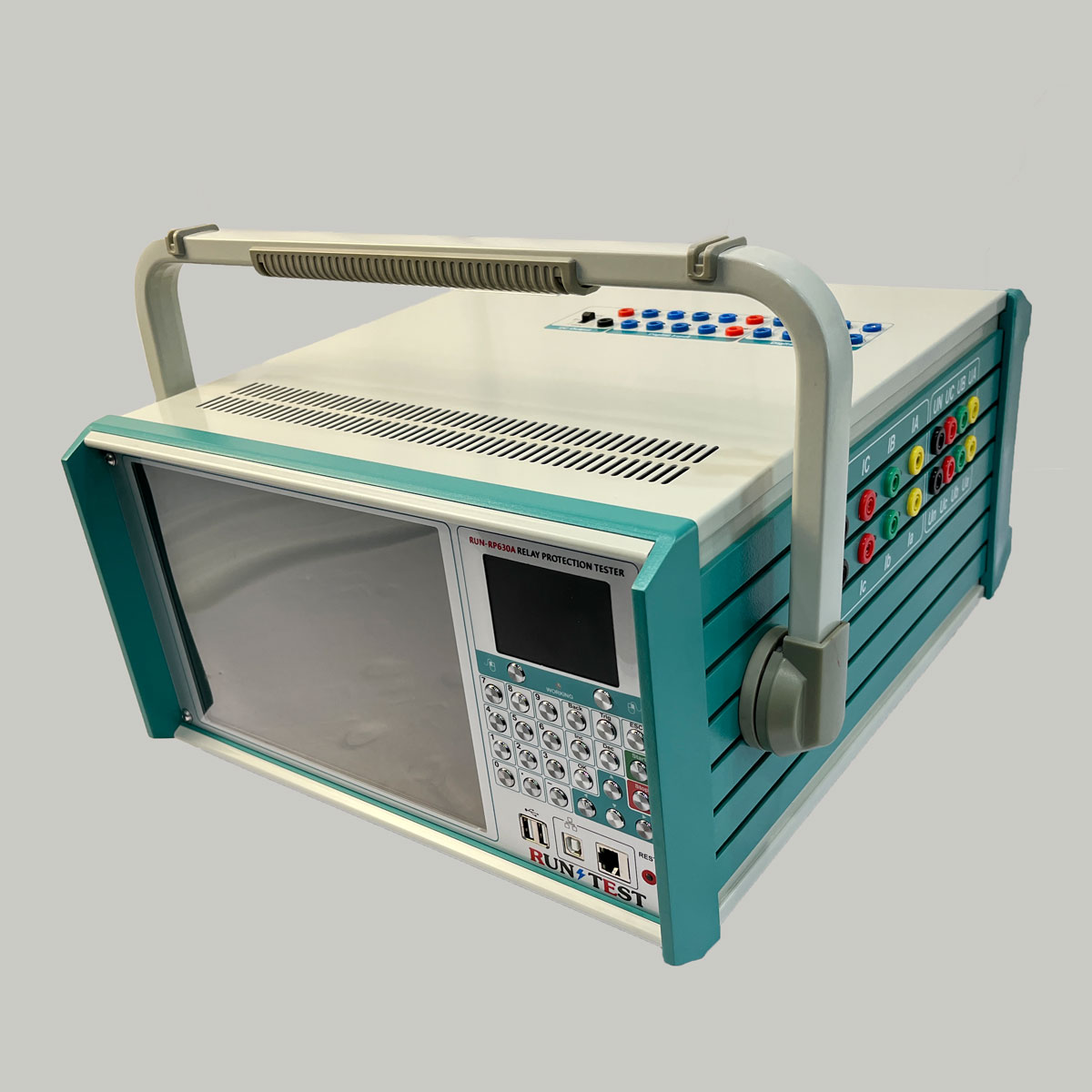

Six Phase Secondary Injection Protection Relay Tester
-

Secondary Injection 3 Phase 40A Microcomputer Protection Relay Tester
-
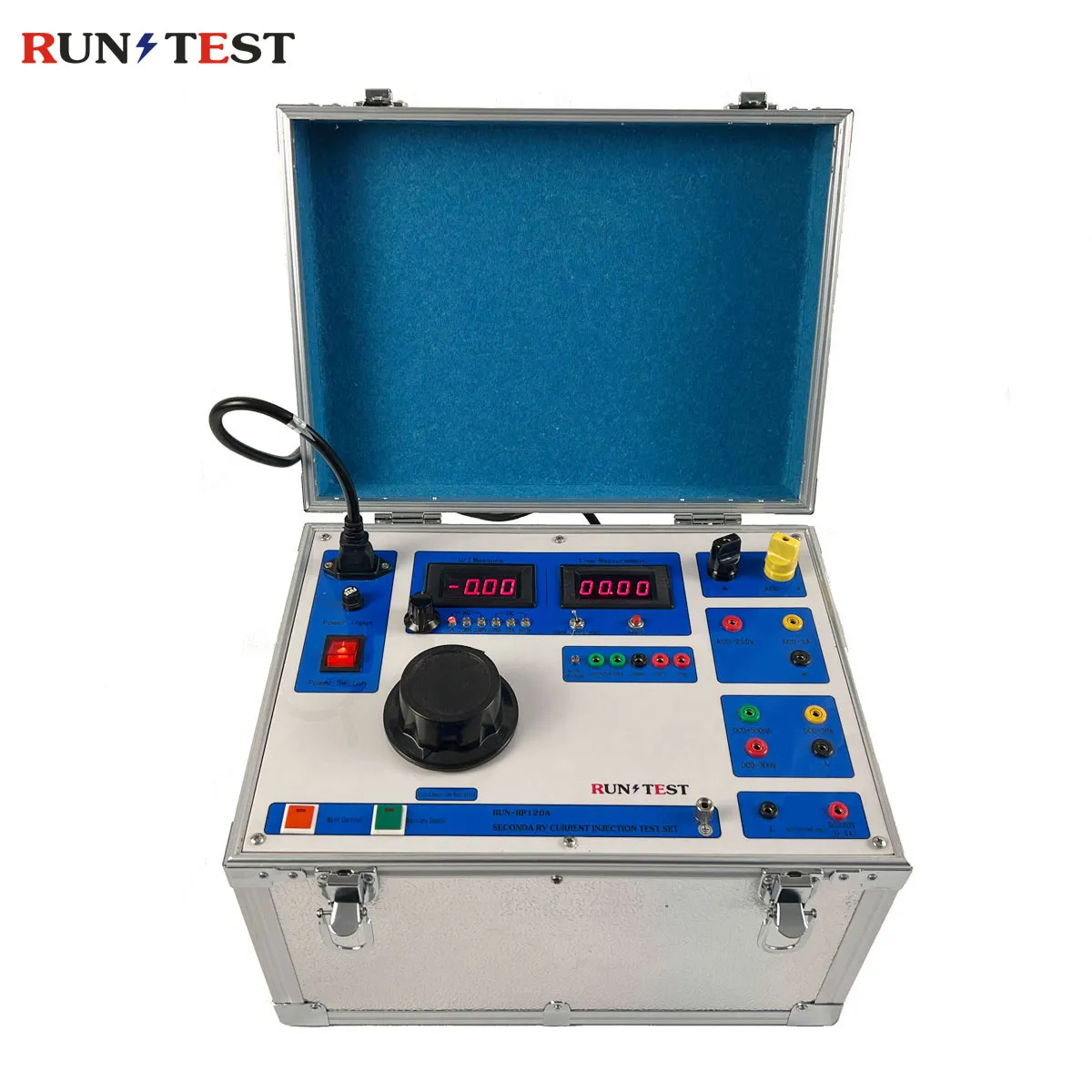

Single Phase Relay Protection Tester
-

CE certificate relay protection testing instrument microcomputer relay protection tester
-

New arrival relay protection testing instrument microcomputer relay tester
-
New 6 Phase Relay Protection Tester
-

Three Phase Protection Relay Test Secondary Current Injection Relay Protective Tester
-
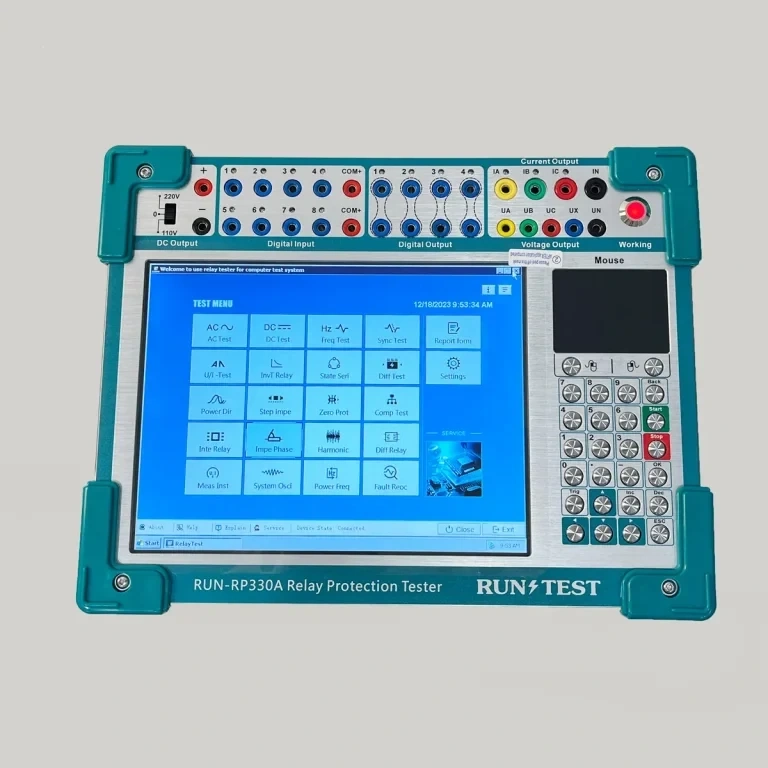

3 Phase Relay Protection Test Set
Relay Protection Test: Key Features and Tests
A relay protection tester creates simulated system faults (such as overcurrent, undercurrent, overvoltage, undervoltage, etc.) and checks how the relay reacts to these conditions. The main goal is to ensure the relay works correctly, coordinates with other protection devices, and responds effectively to faults.
Key Features of Relay Protection Testers
1. Fault Simulation
The tester can replicate any types of wrong doings like a short circuit, excessive voltage, and too low current. It is creating exact fault current and voltage to checking the reaction of the relay.
2. Multi-phase Testing
Most electrical systems use three-phase power, so most testers support multi-phase testing. This is vital for checking relays that protect three-phase systems.
3. Accuracy and Precision
Relay testers should use high precision to measure voltage, current, and timing. These accurate values are important for the relays to work, and therefore, the tester's output must be adequate to reproduce real fault conditions without exception.
4. Testing Different Relay Types
These testers work with various relay types, including overcurrent relays, distance relays, and differential relays. They can test both traditional electromagnetic relays and modern digital relays.
5. Automation
Modern relay testers often use software to automate testing. This software generates detailed reports showing the relay’s response times, tripping behavior, and other performance data.
Types of Tests Performed
1. Functional Tests
We check if the relay reacts to faults as expected and if settings like current or voltage thresholds are correctly configured.
2. Timing Tests
We ensure the relay trips within the correct time limit when a fault occurs.
3. Burden Tests
We measure how the relay operates under different load conditions.
4. Coordination Tests
We ensure relays work together properly in a protection system—for example, making sure downstream relays use time-delayed tripping to avoid unnecessary power outages.
5. Accuracy Tests
We verify the relay’s sensitivity and accuracy in detecting fault conditions.
In actual utilization, the relay protection testers are of vital importance as they are involved in putting, maintaining, and solving relay protective problems in power systems. They assist in the prevention of system failures, and thus in the equipment safety, that the protection system should provide according to the design is not compromised.
